Service Provider Routing and Switching, Professional (JNCIP-SP)

The Service Provider Routing and Switching track allows you to showcase a comprehensive grasp of networking technology and Juniper Networks’ service provider routing and switching systems. The Service Provider Routing and Switching, Professional (JNCIP-SP) – JN0-664 certification is aimed at professionals with extensive expertise in Junos-based routing and switching implementations. This professional-level certification’s written exam assesses your foundational knowledge of advanced routing technologies, as well as your ability to configure and troubleshoot related platforms.
Exam Details
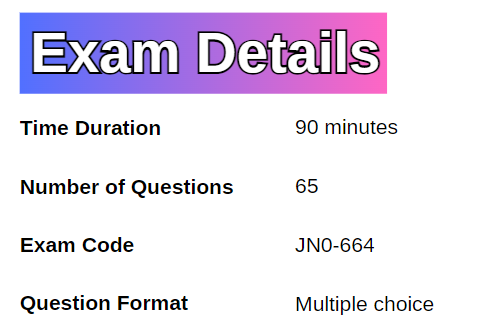
The Service Provider Routing and Switching, Professional (JNCIP-SP) – JN0-664 certification exam has a prerequisite exam JNCIS-SP, and is administered by Pearson VUE. It has a time limit of 90 minutes and consists of 65 multiple-choice questions. The exam uses the software version Junos OS 22.3.
Course Outline
The Service Provider Routing and Switching, Professional (JNCIP-SP) – JN0-664 certification exam covers the following topics:

Topic 1: OSPF
Describe the concepts, operation, or functionality of OSPFv2 and OSPFv3:
- OSPF area types and operations
- Link-state advertisement (LSA) flooding through an OSPF multi-area network
- Designated router/backup designated router operation
- Shortest-path-first (SPF) algorithm
- Metrics, including external metric types
- Summarize and restrict routes
- Virtual links
- OSPFv2 vs. OSPFv3
Given a scenario, demonstrate knowledge of how to configure or monitor single-area or multi-area OSPF:
- Implement OSPF routing policy
Topic 2: IS-IS
Describe the concepts, operation, or functionality of IS-IS:
- IS-IS areas/levels and operations
- Label-switched path (LSP) flooding through an IS-IS multi- area network
- Designated intermediate system (DIS) operation
- SPF algorithm
- Metrics, including wide metrics
- Route summarization and route leaking
Given a scenario, demonstrate knowledge of how to configure or monitor single-area or multi-area IS-IS:
- Implement IS-IS routing policy
Topic 3: BGP
Describe the concepts, operation, or functionality of BGP:
- BGP route selection process
- Next-hop resolution
- BGP attributes—concept and operation
- BGP communities
- Regular expressions
- Multipath
- Multihop
- Load balancing
- Advanced BGP options
- BGP route damping
- BGP flowspec
- Multiprotocol BGP
Describe the concepts, operation, or functionality of BGP scaling mechanisms:
- Route reflection
Given a scenario, demonstrate knowledge of how to configure or monitor BGP:
- Implement BGP routing policy
Topic 4: Class of Service (CoS)
Describe the concepts, operation, or functionality of Junos OS CoS:
- CoS processing on Junos OS devices
- CoS header fields
- Forwarding classes
- Classification
- Packet loss priority
- Policers
- Schedulers
- Drop profiles
- Rewrite rules
Given a scenario, demonstrate knowledge of how to configure or monitor CoS.
Topic 5: IP Multicast
Describe the concepts, operation, or functionality of IP multicast:
- Components of IP multicast, including multicast addressing
- IP multicast traffic flow
- Any-source multicast (ASM) versus source-specific multicast (SSM)
- Reverse path forwarding (RPF)—concept and operation
- Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP)
- Physical Interface Module (PIM) dense mode and sparse mode
- Rendezvous point (RP)—concept, operation, discovery, election
- Source-specific multicast (SSM)—requirements, benefits, address ranges
- Anycast rendezvous point (RP)
Given a scenario, demonstrate knowledge of how to configure or monitor IGMP, PIM dense mode, or PIM sparse mode (including SSM):
- Implement IP multicast routing policy
Topic 6: Layer 3 VPNs
Describe the concepts, operation, or functionality of Layer 3 VPNs:
- Traffic flow—control and data planes
- Full mesh versus hub-and-spoke topology
- VPN-IPv4 addressing
- Route distinguishers
- Route targets
- Route distribution
- Site of origin
- Sham links
- Virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) table-label
- Next-generation multicast virtual private networks (MVPNs)
- Flow of control and data traffic in a MVPN
- Layer 3 VPN scaling
- IPv6 Layer 3 VPNs
- Layer 3 VPN Internet access options
Given a scenario, demonstrate knowledge of how to configure or monitor the components of Layer 3 VPNs.
Describe Junos OS support for carrier-of-carriers or inter-provider VPN models.
Topic 7: Layer 2 VPNs
Describe the concepts, operation, or functionality of BGP Layer 2 VPNs:
- Traffic flow—control and data planes
- Forwarding tables
- Connection mapping
- Layer 2 VPN network layer reachability information (NLRI)
- Route distinguishers
- Route targets
- Layer 2 VPN scaling
Describe the concepts, operation, or functionality of LDP Layer 2 circuits:
- Traffic flow—control and data planes
- Virtual circuit label
- Autodiscovery (AD)
- Layer 2 interworking
Describe the concepts, operation, or functionality of virtual private LAN service (VPLS):
- Traffic flow—control and data planes
- BGP VPLS label distribution
- LDP VPLS label distribution
- Route targets
- VPLS multihoming
- Site IDs
Describe the concepts, operation, or functionality of EVPN:
- Traffic flow—control and data planes
- Media access control (MAC) learning and distribution
- Ethernet VPN (EVPN) multihoming
- BGP EVPN label distribution
Given a scenario, demonstrate knowledge of how to configure, monitor, or troubleshoot Layer 2 VPNs:
- BGP Layer 2 VPNs
- LDP Layer 2 circuits
- EVPNs
- VPLS
Exam FAQs: JNCIP-SP (JN0-664)
Exam General Guidelines
Juniper Networks has established recertification criteria to maintain the high standards of JNCP certifications and ensure the ongoing relevance of certified individuals’ skills. These criteria are applicable across all JNCP certification tracks and are subject to potential revisions.
- Renewing certifications can be achieved by either passing an exam or completing a course at a higher level within the same track. This renewal also extends to all lower-level active certifications within the track, as well as any other active Associate-level certifications.
- Program participants have access to their certification status through CertMetrics and will receive periodic email notifications concerning their certifications. It is the responsibility of certification holders to keep both their certifications and contact information current.
- All JNCP certifications remain active for three years. Failure to renew certifications within this three-year period will result in their expiration.
Study Guide for JNCIP-SP (JN0-664) Exam

1. Understand the Exam Objectives
Thoroughly understanding the objectives of the JNCIP-SP (JN0-664) exam is crucial for effective preparation. These objectives outline the key topics and skills that will be evaluated, providing candidates with a clear roadmap for their studies. By reviewing these objectives, candidates can pinpoint areas that need more attention, allowing them to create a focused study plan and allocate their time and resources wisely. Additionally, being familiar with these objectives helps candidates gauge their preparedness and confidence, ensuring they cover all necessary subjects comprehensively and are well-prepared for the exam.
2. Use Juniper Recommended Training
Advanced Junos Service Provider Routing:
This five-day course offers in-depth instruction on OSPF, IS-IS, BGP, and routing policies. Students will engage with examples, demonstrations, and hands-on labs to learn how to configure, monitor, and troubleshoot the Junos operating system, as well as oversee device and protocol operations. The hands-on labs use Juniper Networks vMX Series Routers, but the skills taught are relevant to other Juniper hardware platforms running Junos OS. The course material is based on Junos OS Release 23.2.
This three-day course equips students with the skills to configure and troubleshoot MPLS-based Layer 2 virtual private networks (VPNs). The curriculum covers MPLS Layer 2 VPN concepts, including BGP Layer 2 VPNs, LDP Layer 2 circuits, forwarding equivalence class (FEC) 129, virtual private LAN service (VPLS), Ethernet VPN (EVPN), and Inter-AS MPLS VPNs. Additionally, it addresses Junos OS-specific implementations of Layer 2 VPN instances, VPLS, and EVPNs. Based on Junos OS Release 21.4R1.12, the course features hands-on labs that provide extensive CLI configuration practice, examples of common errors, and troubleshooting techniques to resolve them.
This three-day course provides students with in-depth knowledge of MPLS-based Layer 3 VPN (L3VPN) concepts and configuration examples. It covers topics such as MPLS L3VPN fundamentals, scaling L3VPNs, Internet access, interprovider L3VPNs, and multicast for L3VPNs. The course also includes specific implementations of Layer 3 VPNs on the Junos operating system (OS). Through a series of hands-on labs, participants will gain practical experience configuring and monitoring L3VPNs on Junos OS devices. The labs utilize Juniper Networks vMX Series devices running Junos OS Release 22.1R1.10 but are also applicable to other MX Series devices.
3. Use Juniper TechLibrary for Reference
Juniper TechLibrary is vital for mastering Juniper Networks technologies. This comprehensive library offers a vast collection of technical documents, guides, configuration examples, and troubleshooting resources specifically designed for Juniper products and solutions. By understanding the TechLibrary, users can understand the details of Juniper devices and software, including their functionalities, configurations, and best practices. Browsing through this resource helps individuals find documentation relevant to their specific interests or expertise, whether in routing, switching, security, automation, or cloud solutions.
4. Join Study Groups
Joining study groups or communities can greatly enhance your learning experience. By participating in groups that match your interests or certification goals, you engage in discussions, share knowledge, and work together with individuals. This interaction exposes you to a variety of perspectives and expertise from other members. Additionally, these communities provide a supportive atmosphere where individuals help, motivate, and mentor one another, promoting mutual growth and understanding.
5. Take Practice Tests
Taking practice exams is highly advantageous because it highlights your strengths and identifies areas that need improvement. This self-evaluation boosts your ability to answer questions effectively and improves your time management skills for the actual exam. It’s advisable to take these tests after completing each topic to reinforce your understanding of the material. Regular practice exams also help you become familiar with the exam format and question types, which can reduce anxiety and increase confidence. By consistently reviewing your performance on these tests, you can develop a targeted study plan that addresses your weaknesses and enhances your overall exam readiness.



