In today’s fast-evolving tech landscape, cloud computing has become the backbone of modern software development. Companies are increasingly adopting DevOps practices to streamline application delivery, improve reliability, and reduce downtime. Among cloud platforms, Google Cloud Platform (GCP) stands out for its robust DevOps tools and services, making the Google Cloud DevOps Engineer certification a highly sought-after credential.
This certification validates your ability to design and implement efficient DevOps practices on GCP. It proves that you can manage CI/CD pipelines, deploy containerized applications, monitor services effectively, and ensure reliability and scalability in production environments. For IT professionals, system administrators, and cloud engineers, this exam is more than just a certificate—it’s a career accelerator. Passing it demonstrates not only technical proficiency but also a practical understanding of DevOps workflows in real-world cloud environments.
In this blog, we will break down everything you need to know to prepare for the Google Cloud DevOps Engineer Exam in 2025. From understanding the exam structure and key topics to practical study strategies and resources, this guide will help you approach your preparation with confidence. Whether you’re a beginner in GCP or an experienced DevOps professional, the tips here are tailored to maximize your chances of success.
Certifications have become very essential for career development. A Professional Cloud DevOps Engineer’s job is to make sure that software development operations run smoothly while balancing service reliability and speed. They are experts in using the Google Cloud Platform to create pipelines for delivering software, deploying and keeping an eye on services, and handling and learn from incidents. We need to adopt ‘excellence’ as a survival mechanism in the corporate industry. Therefore, certifications help us to get an edge over others and make our performance better. In today’s world, businesses prefer to hire certified professionals, and certifications demonstrate your dedication, commitment to goals, and your drive to achieve them.

Certifications like the Google Cloud DevOps Engineer Exam can be difficult to crack without proper guidance. These kinds of certifications can help you in scoring your dream job and further climb up the corporate ladder. So, if you are planning to crack the Google Cloud DevOps Engineer Exam, this is the right destination for you. This article will serve you with all the details related to the exam, along with a handful of preparatory resources. Let us get underway.
Why Google Cloud DevOps Engineer Exam?
A Professional Cloud DevOps Engineer ensures that the development process runs smoothly, balancing service reliability and delivery speed. The need for Certified Google DevOps Professionals is growing rapidly.
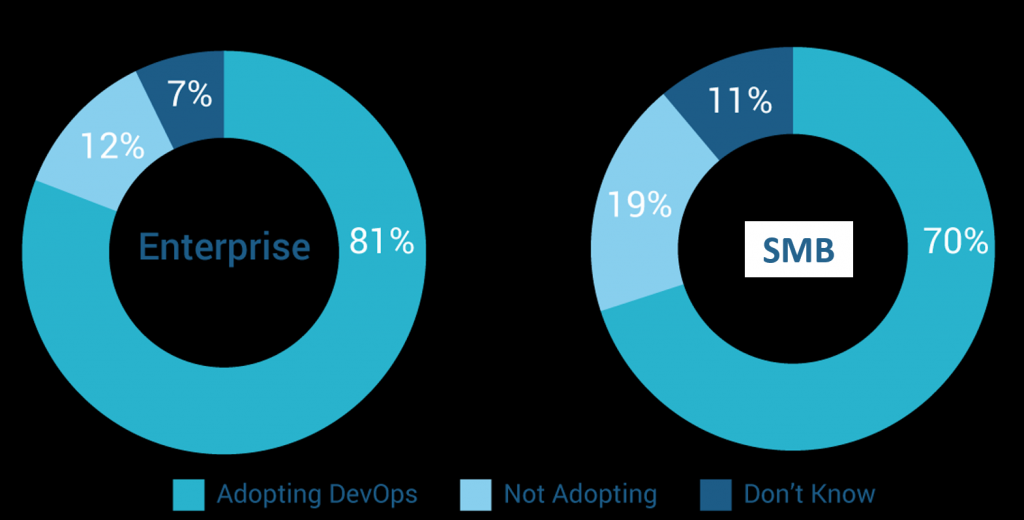
Now, when we see the results clearly 81% of the enterprises are using DevOps practices, along with 70% of small to medium businesses. Moreover, there are various reasons for such an increase in the adoption of DevOps practices, including –
- Firstly, the automated delivery pipelines help the release of small features more frequently
- Secondly, the increased adoption of Microservice architecture
- Next, Reduced failure rate of new releases
- Also, the shortened lead time between fixes
- Lastly, a faster mean time to recovery in the event of a new release crashing
Let us now move to the exam overview for the basic details of the exam to help you prepare for the final exam.
Exam overview
The Google Cloud DevOps Engineer Exam consists of 50 questions, which have to be answered in 120 minutes. The exam costs $200 exclusive of taxes; taxes will be applicable as per region, and prices may also vary from time to time. Also, the exam is available only in the English language, and the type of questions asked are multiple-choice and multiple-select questions. Subsequently, there are no prerequisites for the exam; however, Google recommends experience of three+ years of industry experience, including one+ years managing solutions on GCP.
Exam Details
| Exam name | Google Cloud DevOps Engineer Exam |
| Exam code | GCP |
| No. of questions | 50 |
| Language available | English |
| Experience required | Three+ years of industry experience including one+ years managing solutions on GCP |
| Question format | Multiple choice and multiple select |
| Exam price | $200 plus taxes |
| Registration platform | Google Cloud Webassessor |
Related Exam Details
You can register for the exam by creating a new Google Webassessor account. You have to select your exam and then your language and also test center. There is no fixed passing score for the Google Cloud DevOps Engineer Exam, as the panel determines the passing score after the exam.
Now that we are done with the details of the exam, let us move forward to the syllabus in detail.
Who should take this Exam?
The Google Cloud DevOps Engineer Exam is designed for professionals who are actively involved in deploying, managing, and optimizing applications on Google Cloud. If you’re working with cloud infrastructure and DevOps practices, this certification can significantly boost your career.
Target Audience:
- DevOps Professionals: Individuals responsible for automating deployments, managing CI/CD pipelines, and ensuring system reliability will benefit the most.
- Cloud Engineers: Those working with GCP services such as Compute Engine, Kubernetes Engine, Cloud Build, and Cloud Monitoring can validate their practical knowledge.
- System Administrators & IT Operations: Professionals managing cloud-based systems who want to enhance their skills in cloud automation, monitoring, and scalability.
- Software Developers with Cloud Exposure: Developers who participate in deploying applications and maintaining cloud environments will gain credibility by demonstrating operational expertise.
Prerequisites:
- Hands-on experience with Google Cloud Platform services.
- Familiarity with CI/CD pipelines, containerization (Docker, Kubernetes), and infrastructure as code (Terraform, Deployment Manager).
- Basic understanding of monitoring, logging, and troubleshooting in cloud environments.
Benefits of Certification:
- Career Advancement: Employers increasingly value certified professionals who can bridge the gap between development and operations.
- Validation of Skills: The certification proves you have the practical knowledge to manage and optimize DevOps workflows on GCP.
- Higher Earning Potential: Certified cloud professionals often command better salaries and more opportunities for leadership roles.
- Confidence in Real-World Scenarios: By preparing for the exam, you gain hands-on experience that directly applies to day-to-day cloud operations.
This exam is ideal for anyone aiming to strengthen their DevOps expertise on Google Cloud, whether you’re starting your cloud journey or looking to formalize years of hands-on experience.
Google Cloud DevOps Engineer Exam Documentation and Course Outline
There are 5 major testing areas as prescribed by Google. The testing areas are as follows:
Topic 1: Bootstrapping a Google Cloud organization for DevOps
1.1 Designing the overall resource hierarchy for an organization. Considerations include:
- Projects and folders
- Shared networking
- Identity and Access Management (IAM) roles and organization-level policies
- Creating and managing service accounts
1.2 Managing infrastructure as code. Considerations include:
- Infrastructure as code tooling (e.g., Cloud Foundation Toolkit, Config Connector, Terraform, Helm)
- Making infrastructure changes using Google-recommended practices and infrastructure as code blueprints
- Immutable architecture
1.3 Designing a CI/CD architecture stack in Google Cloud, hybrid, and multi-cloud environments. Considerations include:
- CI with Cloud Build
- CD with Google Cloud Deploy
- Widely used third-party tooling (e.g., Jenkins, Git, ArgoCD, Packer)
- Security of CI/CD tooling
1.4 Managing multiple environments (e.g., staging, production). Considerations include:
- Determining the number of environments and their purpose
- Creating environments dynamically for each feature branch with Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) and Terraform
- Anthos Config Management
Topic 2: Building and implementing CI/CD pipelines for a service
2.1 Designing and managing CI/CD pipelines. Considerations include:
- Immutable artifacts with Container Registry (Google Documentation: Help secure software supply chains on Google Kubernetes Engine, Managing images)
- Artifact management with Artifact Registry
- Deployment to hybrid and multi-cloud environments (e.g., Anthos, GKE)
- CI/CD pipeline triggers
- Testing a new application version in the pipeline
- Configuring deployment processes (e.g., approval flows) (Google Documentation: Setting up a CI/CD pipeline for your data-processing workflow)
- CI/CD of serverless applications
2.2 Implement CI/CD pipelines:
- Auditing and tracking deployments (e.g., Artifact Registry, Cloud Build, Google Cloud Deploy, Cloud Audit Logs)
- Deployment strategies (e.g., canary, blue/green, rolling, traffic splitting)
- Rollback strategies
- Troubleshooting deployment issues
2.3 Managing CI/CD configuration and secrets. Considerations include:
- Secure storage methods and key rotation services (e.g., Cloud Key Management Service, Secret Manager) (Google Documentation: Cloud storage)
- Secret management
- Build versus runtime secret injection
2.4 Secure the deployment pipeline:
- Vulnerability analysis with Container Registry (Google Documentation: Getting vulnerabilities and metadata for images)
- Binary Authorization (Google Documentation: Binary Authorization)
- IAM policies per environment (Google Documentation: Policy)
Section 3: Applying site reliability engineering practices to a service
3.1 Balancing change, velocity, and reliability of the service. Considerations include:
- Discovering SLIs (e.g., availability, latency)
- Defining SLOs and understanding SLAs
- Error budgets
- Toil automation
- Opportunity cost of risk and reliability (e.g., number of “nines”)
3.2 Managing service lifecycle. Considerations include:
- Service management (e.g., introduction of a new service by using a pre-service onboarding checklist, launch plan, or deployment plan, deployment, maintenance, and retirement)
- Capacity planning (e.g., quotas and limits management)
- Autoscaling using managed instance groups, Cloud Run, Cloud Functions, or GKE
- Implementing feedback loops to improve a service
3.3 Ensuring healthy communication and collaboration for operations. Considerations include:
- Preventing burnout (e.g., setting up automation processes to prevent burnout)
- Fostering a culture of learning and blamelessness
- Establishing joint ownership of services to eliminate team silos
3.4 Mitigating incident impact on users. Considerations include:
- Communicating during an incident
- Draining/redirecting traffic
- Adding capacity
3.5 Conducting a postmortem. Considerations include:
- Documenting root causes
- Creating and prioritizing action items
- Communicating the postmortem to stakeholders
Topic 4: Implementing service monitoring strategies
4.1 Manage logs:
- Collecting structured and unstructured logs from Compute Engine, GKE, and serverless platforms using Cloud Logging
- Configuring the Cloud Logging agent
- Collecting logs from outside Google Cloud
- Sending application logs directly to the Cloud Logging API
- Log levels (e.g., info, error, debug, fatal)
- Optimizing logs (e.g., multiline logging, exceptions, size, cost)
4.2 Managing metrics with Cloud Monitoring. Considerations include:
- Collecting and analyzing application and platform metrics
- Collecting networking and service mesh metrics
- Use metric explorer for ad hoc metric analysis (Google Documentation: Metrics Explorer)
- Creating custom metrics from logs
4.3 Managing dashboards and alerts in Cloud Monitoring. Considerations include:
- Creating a monitoring dashboard
- Filtering and sharing dashboards
- Configuring alerting
- Defining alerting policies based on SLOs and SLIs
- Automating alerting policy definition using Terraform
- Using Google Cloud Managed Service for Prometheus to collect metrics and set up monitoring and alerting
4.4 Managing Cloud Logging platform. Considerations include:
- Enabling data access logs (e.g., Cloud Audit Logs)
- Enabling VPC Flow Logs
- Viewing logs in the Google Cloud console
- Using basic versus advanced log filters
- Logs exclusion versus logs export
- Project-level versus organization-level export
- Managing and viewing log exports
- Sending logs to an external logging platform
- Filtering and redacting sensitive data (e.g., personally identifiable information [PII], protected health information [PHI])
4.5 Implementing logging and monitoring access controls. Considerations include:
- Restricting access to audit logs and VPC Flow Logs with Cloud Logging
- Restricting export configuration with Cloud Logging
- Allowing metric and log writing with Cloud Monitoring
Topic 5: Optimizing service performance
5.1 Identify service performance issues:
- Using Google Cloud’s operations suite to identify cloud resource utilization
- Interpret service mesh telemetry (Google Documentation: The service mesh era)
- Troubleshooting issues with compute resources
- Troubleshooting deploy time and runtime issues with applications
- Troubleshooting network issues (e.g., VPC Flow Logs, firewall logs, latency, network details (Google Documentation: VPC Flow Logs overview, Using VPC Flow Logs, Using Firewall Rules Logging)
5.2 Implementing debugging tools in Google Cloud. Considerations include:
- Application instrumentation (Google Documentation: Cloud Monitoring)
- Cloud Logging
- Cloud Trace
- Error Reporting
- Cloud Profiler
- Cloud Monitoring
5.3 Optimize resource utilization and costs:
- Preemptible/Spot virtual machines (VMs)
- Committed-use discounts (e.g., flexible, resource-based)
- Sustained-use discounts
- Network tiers
- Sizing recommendations
Let us now move to a very important part i.e. exam preparation resources.
Preparatory resources for Google Cloud DevOps Engineer Exam
There are numerous resources available for preparation, but you have to be very careful for choosing the best for you, as they will determine your performance in the exam. Let us look at a handful of them –
Official Site and Resources Available
The official site, firstly, provides insights into various aspects of the exam. Make sure to visit the official site before the exam to gather the information about the exam and, subsequently, during your preparation days too, to keep yourself updated regarding the exam. The official site also provides you with various online course options, instructor-led training options, and hands-on practice material. These are one of the reliable and best materials you can use for the preparation. You can also use the cloud platform to clear your doubts and to extend your knowledge regarding any matter.
Books are the Best Friends
Books are the most preferred resource by many of us. They are handy and serve as the best resource to many of us. You can refer to any of the books or e-book that you find comfortable to read and understand. Also, books are easily available in the libraries or the book stores near you. Some of the books that you can refer to for the Google Cloud DevOps Engineer Exam are:
- Firstly, Google Professional Cloud DevOps Engineer 33 Exam Prep Questions
- Secondly, Terraform: Up & Running: Writing Infrastructure as Code
- Thirdly, Kubernetes – A Complete DevOps Cookbook: Build and manage your applications, orchestrate containers, and deploy cloud-native services
- Subsequently, Hands-On Security in DevOps: Ensure continuous security, deployment, and delivery with DevSecOps
- Finally, Hands-on Security in DevOps
Online Courses and Instructor-led Trainings
Online courses and instructor-led trainings are one of the best ways to prepare. These kinds of classes are interactive enough and help you in clearing your doubts. You can also find test series with them, which will help you improve. These classes also provide you with very good and reliable content, which can be used for preparation. There are many educational sites that provide you with reliable classes and a 100% exam pass guarantee.
Practice Exams and Test Series
These are the most essential parts of the preparation. Practice with the help of sample papers and taking test series to improve your accuracy and way of answering the questions. They also help you determine the various areas of preparation that are weak and need more practice. On the other hand, it also helps you find your strengths. In short, practice papers and test series help you in taking your SWOT analysis. There are many reliable sites that provide you with good content. So, let’s Start Practicing for the Google DevOps Engineer Exam!
Other Reliable Resources for Preparation
There are many other resources as libraries, e-labs, and classroom classes etc., which can help you in preparing well. Most importantly, you have to pay more focus on the self-study part to succeed. Make your strategy and also try to implement that as strictly as possible. Now that you are well versed with the preparatory resources and all the details of the exam, therefore, let us now wind up so that you can start preparing to qualify for the exam.
Expert Advice
Therefore, to sum up, achieving the certification is not so a challenging task if you take the preparation part with full dedication and put in full effort to crack the exam. The certification will add value to your skill set and will also help you stand out in the crowd. This Google Cloud DevOps Engineer Exam will surely upgrade your resume and help you in achieving your dreams.
All the best.


